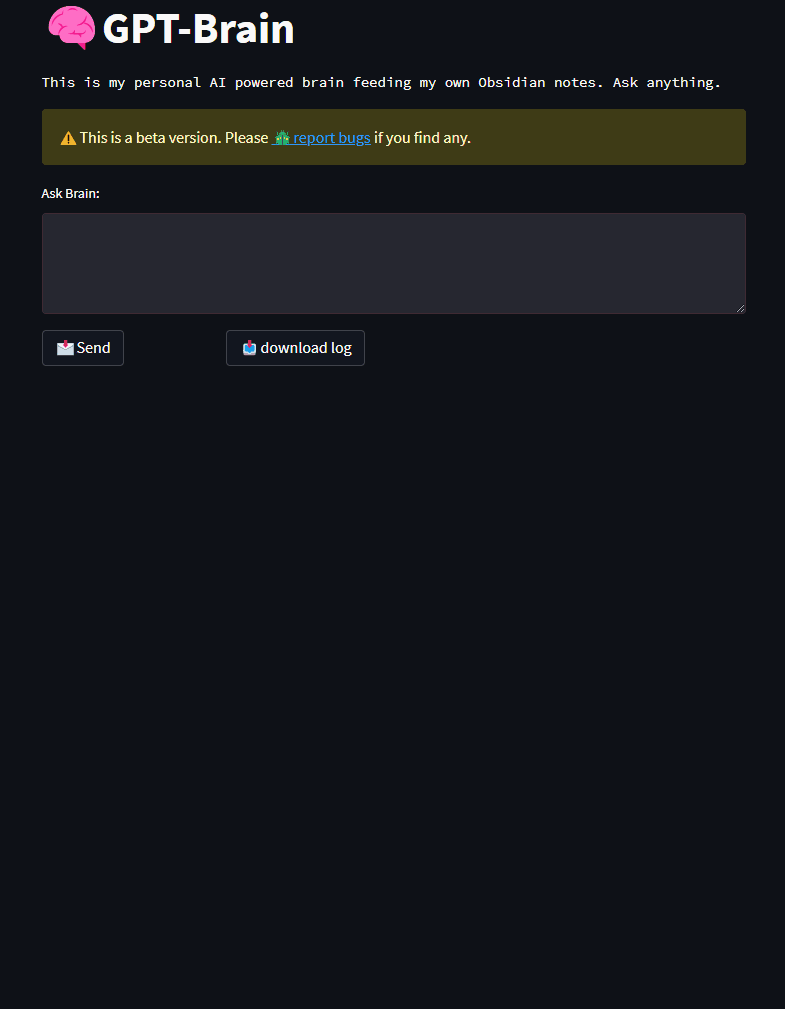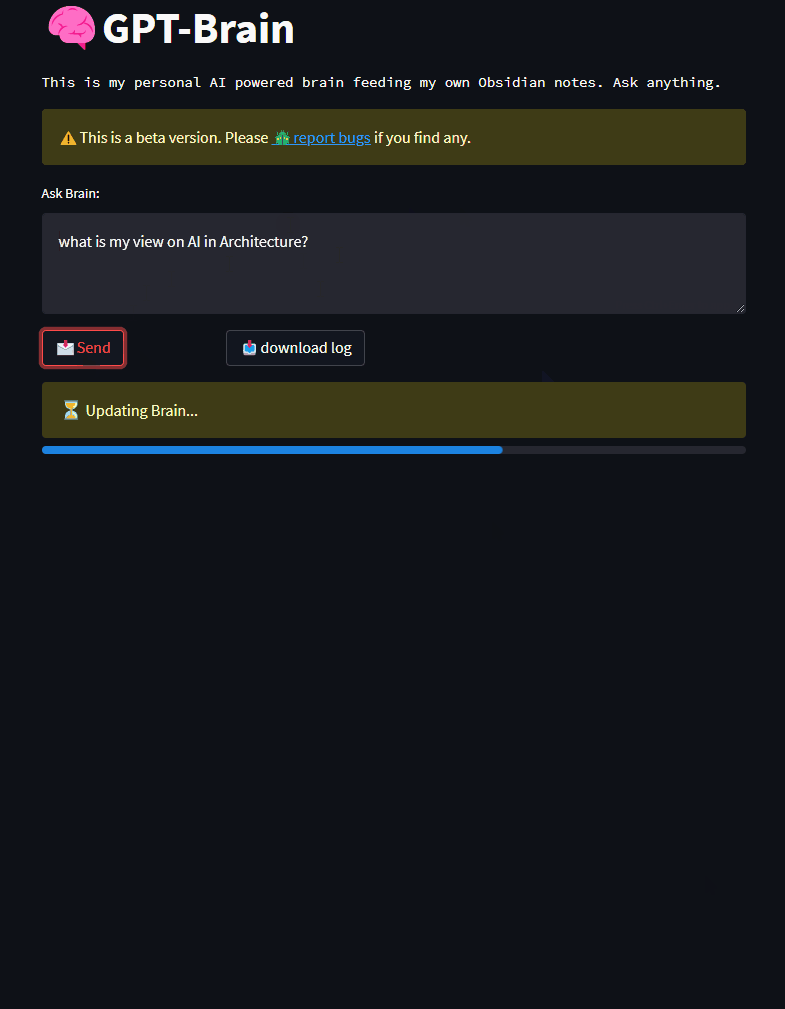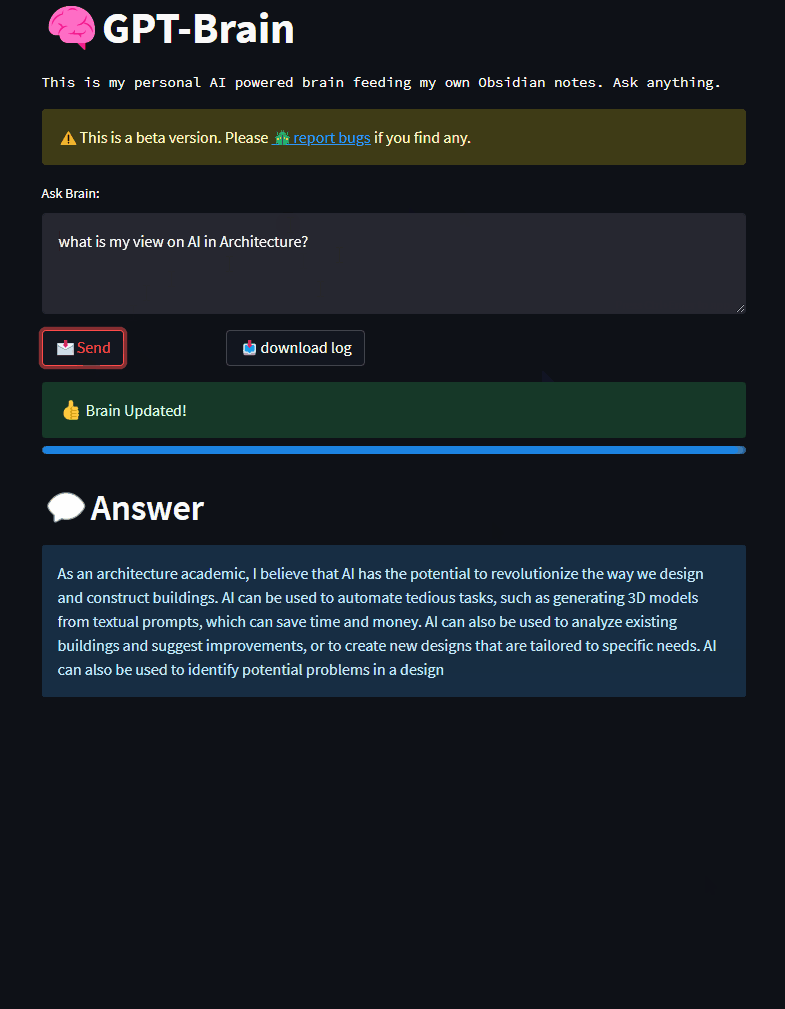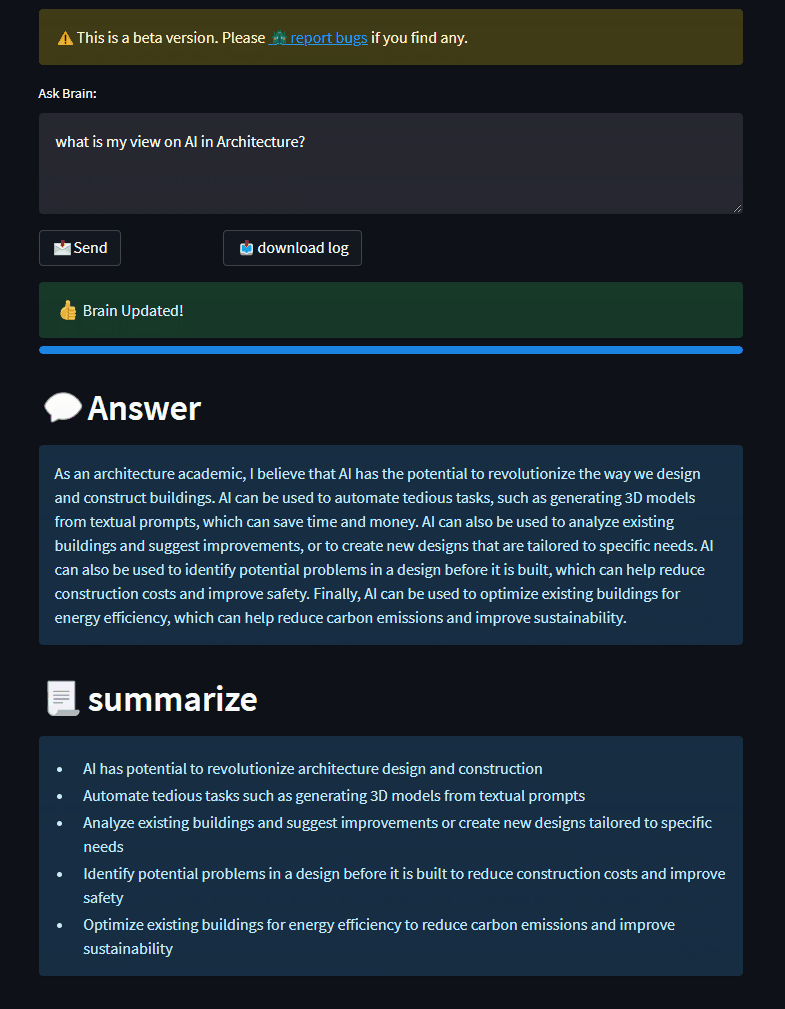
This project serves as an example of how to use the Open LMS development box
that is published to Atlas. While you can use this project directly, it is meant as a starting
point for your own Vagrantfile where you can customize the Open LMS development box
using Vagrant provisioning. So, forking of this project
for customization is encouraged.
This project does not attempt to provide the ideal development environment for every Moodle developer.
The Open LMS team simply wants to share their development box and provide some documentation on how
to use it. So, please keep that in mind when filing issues and pull requests.
The Open LMS development box has the following technologies installed:
- Ubuntu is the operating system
- Nginx with PHP-FPM
- PHP
- Redis
- Git
- NodeJS, NPM and Grunt installed globally
- Chrome and Firefox
- Selenium for Behat
- And other various tools required by Moodle.
For the adventurous, you can explore the details of the box creation process in this project.
To install and use this project:
- Clone this project:
git clone https://github.com/open-lms-open-source/moodle-vagrant-example.git ~/vagrant - Install recommended versions of Vagrant and VirtualBox for the latest box release on Vagrant Cloud.
- Install Vagrant Host Manager Plugin:
vagrant plugin install vagrant-hostmanager - Open your terminal and from within this project, run:
vagrant up
After the vagrant up command completes, your virtual machine will be ready. You can use vagrant ssh
to access it.
Always confirm that you have the correct versions of Vagrant and VirtualBox installed. Refer to the
above install section for the correct versions. If you upgrade Vagrant, be sure to upgrade the plugins:
> vagrant plugin update
Ensure that this project is up-to-date, use the following:
> cd /path/to/this/project
> git fetch origin
> git merge --ff-only origin/master
If the base box is updated, then you will have to re-create your virtual machine to get the updated box. Before
doing that, backup any data on the virtual machine first, like databases and data directories. See the
“Vagrant management” section on how to backup multiple databases.
Once backups are complete, do the following:
> vagrant box update
> vagrant destroy
> vagrant up
Optionally, you can delete old versions of the box to free up disk space:
> vagrant box prune
To access your virtual machine:
> vagrant ssh
If you are not going to be using your virtual machine for a while or are going to be turning off
your computer, then you can shutdown the virtual machine:
> vagrant halt
Then, when you want to use it again:
> vagrant up
If you need to restart it:
> vagrant reload
Lastly, if you ever need to start fresh, you can delete your virtual machine, but before
doing so, backup any data that is in the box. Most importantly, your MySQL databases:
> vagrant ssh
> mysqldump -u root -p --databases database1 database2 database3 > /vagrant/mysql.bak.sql
Enter password: [Type in root]
Replace database1 database2 database3 with a list of databases you wish to backup. In addition
archive any of your Moodle data directories as well.
Once backups are complete, you can destroy your virtual machine:
> vagrant destroy
Lastly, you can re-create the virtual machine and restore your databases:
> vagrant up
> vagrant ssh
> mysql -u root -p < /vagrant/mysql.bak.sql
Enter password: [Type in root]
From your host machine with an application like Sequel Pro:
- Host: 0.0.0.0
- Username: root
- Password: root
From within the virtual machine:
> vagrant ssh
> mysql -u root -p
Enter password: [Type in root]
Connect to MySQL using one of the methods mentioned above, then execute the following SQL:
CREATE DATABASE `database-name` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
Replace database-name with the database name you would like to create.
The Moodle data directories can be created under the following directories:
/srv/moodledata//vagrant/moodledata/
The /srv/moodledata location is in the virtual machine itself. This is generally
faster and since they are stored in the virtual machine, they are deleted if the
machine is ever destroyed. This can be good or bad depending on how you like to manage things.
The /vagrant/moodledata/ location is in the NFS mount. This is generally slower,
but it makes the data directories accessible to your host machine and they are not
deleted if the virtual machine is ever destroyed.
Example of how to create a new one, use the following commands:
> vagrant ssh
> mkdir /srv/moodledata/dirname
> chmod 777 /srv/moodledata/dirname
Replace dirname with the directory name you would like to create.
First, clone the Moodle repository into www/moodle directory.
> git clone git://github.com/moodle/moodle.git www/moodle
Next, create a database and data directory for the site. Follow
the steps in above sections to do this.
Lastly, go to moodle.test in your browser and
follow the instructions to install Moodle.
Note: you can install a second Moodle site into www/core-moodle
and access it via core-moodle.test. For example,
you may want to install your customized version of Moodle in www/moodle
and install the core version of Moodle in www/core-moodle.
Also note: the site configs for these directories are in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
where you can add new sites or modify existing ones.
You must install a XDebug extension in your browser and turn on debugging in the browser.
Then in an IDE like PHPStorm, you can listen for debug connections.
To profile a page, do the following:
- Add XDEBUG_PROFILE=1 to your URL.
- Refresh/rerun the page to generate the profile.
- The profiles are stored in the
/srv/xdebug-profilesdirectory in the virtual machine. - Visit webgrind.test to view and delete profiles.
If you would like to use MailHog then follow these steps:
- Edit your config file.
- Comment out the
$CFG->noemaileverline. - Ensure you have this config:
$CFG->smtphosts = '0.0.0.0:1025'; - Purge caches.
MailHog will now capture any emails sent from Moodle and is available on port 8025, EG: http://moodle.test:8025
First, you must update your config file with the following:
$CFG->behat_prefix = 'behat_';
$CFG->behat_dataroot = '/srv/moodledata/behat_moodledata';
$CFG->behat_wwwroot = $CFG->wwwroot.':9090';
// $CFG->behat_faildump_path = '/vagrant/www/behat_screenshots'; // Uncomment for screenshots.
$CFG->behat_profiles = [
'default' => [
'browser' => 'chrome',
'wd_host' => 'http://localhost:4444/wd/hub',
],
'firefox' => [
'browser' => 'firefox',
'wd_host' => 'http://localhost:4444/wd/hub',
]
];
Next, initialize the testing environment:
> vagrant ssh
> cd /vagrant/www/moodle
> php admin/tool/behat/cli/init.php
Take note of the output at the end of this script, it will tell you where your
behat.yml file is located. From now on, this will be referred to as /path/to/behat.yml
Finally, the tests can be run with the following:
> vendor/bin/behat --config /path/to/behat.yml
The above will run all of the Behat tests, which is probably not wanted. You can pass
an additional argument to the behat command, like a directory of feature files, a single
feature file, etc. See vendor/bin/behat -h for more details.
By default, Behat is using Chrome. To use Firefox, use -p firefox.
At time of writing though, Chrome was the fastest browser and has full support.
If you make any sort of configuration changes or add additional tests, you will most likely
need to regenerate the behat.yml file. To do that, run these commands:
> vagrant ssh
> cd /vagrant/www/moodle
> php admin/tool/behat/cli/util.php --enable
See Acceptance testing and
Acceptance testing browsers
for more information.
To connect to the default database to install Moodle use the following connection details:
$CFG->dbtype = 'pgsql';
$CFG->dblibrary = 'native';
$CFG->dbhost = '0.0.0.0';
$CFG->dbname = 'postgres';
$CFG->dbuser = 'postgres';
$CFG->dbpass = 'root';
To create a new database:
> psql -c "create database database_name;" -U postgres template1
To access Postresql from the CLI:
> vagrant ssh
> psql -U postgres
Use this feature to access your virtual machine from any other device, including other
virtual machines. See help document for more
details.
Warning: this makes your virtual machine available to the public, but they of course
need to know the exact details to actually connect. These shares should only last
for around eight hours and expire whenever you kill the vagrant share
command.
- To start sharing, use
vagrant share - The above command will output a URL, you must edit your config
file and update the$CFG->wwwrootwith the URL.
To stop Vagrant share, just go to the terminal window where you started
it and hit control+c to exit the command. Don’t forget to revert your
changes to the config file.
Also, a current limitation of Vagrant share is that you will only be able to
access the Moodle site and not the other virtual hosts provided by your
virtual machine.

https://github.com/open-lms-open-source/moodle-vagrant-example